Answer: 0.077 M
Step-by-step explanation:
Expression for rate law for first order kinetics is given by:
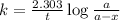
where,
k = rate constant =
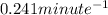
t = time taken for decay process = 10 minutes
a = initial amount of the reactant= 0.859 M
a - x = amount left after decay process =?
Putting values in above equation, we get:
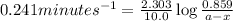
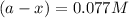
Thus the concentration of a after 10.0 minutes is 0.077 M.