Answer: The final pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to the volume change and directly proportional to temperature change.
Explanation:
1) Boyle's Law: This law states that pressure is inversely proportional to the volume of the gas at constant temperature and number of moles.
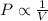 (At constant temperature and number of moles)
(At constant temperature and number of moles)
2) Charles' Law: This law states that volume is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas at constant pressure and number of moles.
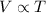 (At constant pressure and number of moles)
(At constant pressure and number of moles)
The combined gas equation is,
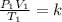
Thus pressure and volume bear inverse relationship but volume and temperature bear direct relationship.