The resistance of a wire is given by
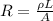
where
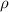
is the resistivity of the material, L the length of the wire and A its cross-sectional area.
In the problem,
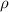
and L remain the same, while A changes because the radius changes. The area is given by:
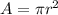
This means that if we double the radius (2r), the area becomes
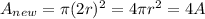
And therefore, the new value of the resistance is
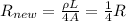
So, when the radius is doubled, the resistance becomes
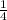
of its original value.