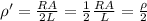The resistivity
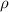
of a wire is related to its length L by the following relationship:
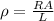
where R is the resistance of the wire, and A its cross-sectional area.
Assuming that the resistance R and the area A are the same for the two wires, we can see from the formula that, if the length L is doubled, then the resistivity
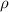
becomes half of the original value. In fact, replacing L with 2 L we get