Answer:
Option A is correct.
Yes, it is true that the triangles shown are congruent.
Explanation:
Labelled the diagram as shown below in the attachment:
In triangle ABC and triangle PQR
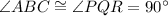 [Angle]
[Angle]
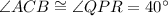 [Angle]
[Angle]
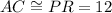 units [Side]
units [Side]
AAS(Angle-Angle-Side) postulates states that the two angles and the non- included side of one triangle are congruent to the two angles and the non-included side of the other triangle., then the triangles are congruent.
Then, by AAS
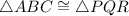
Therefore, the given triangles shown must be congruent.