Answer:
Δ
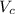 = 7.415 10⁻⁶ m³ (7.415 10⁻³ L)
= 7.415 10⁻⁶ m³ (7.415 10⁻³ L)
Step-by-step explanation:
This problem must find the change in volume of coffee and pyrex, the expression
ΔV = V₀ β ΔT
The expansion coefficients are
Water Volumetry β = 207 10⁻⁶ C⁻¹
Pyrex Linear α = 3.2 10⁻⁶ C⁻¹
In general, for solids the solids find the linear expansion coefficient tabulated, but the linear volumetric coefficient is related
β = 3 α
Let's calm the volume change for the pyrex glass
Δ
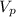 = V₀ 3α ΔT
= V₀ 3α ΔT
Δ
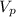 = 0.50 10⁻³ 3 3.2 10⁻⁶ (92-18)
= 0.50 10⁻³ 3 3.2 10⁻⁶ (92-18)
Δ
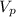 = 3.552 10⁻⁷ m³
= 3.552 10⁻⁷ m³
We look for the change in volume for coffee that is equal to that of water
Δ
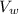 = 0.50 10⁻³ 210 10⁻⁶ (92-18)
= 0.50 10⁻³ 210 10⁻⁶ (92-18)
Δ
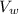 = 7.77 10⁻⁶ m³
= 7.77 10⁻⁶ m³
The amount of spilled coffee is the difference in volumes
Δ
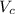 = Δ
= Δ
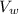 - Δ
- Δ
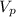
Δ
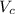 = 7.77 10⁻⁶ - 3.552 10⁻⁷
= 7.77 10⁻⁶ - 3.552 10⁻⁷
Δ
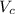 = 7.415 10⁻⁶ m³
= 7.415 10⁻⁶ m³
Let's reduce to liters
Δ
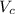 = 7.415 10⁻⁶ m³ (1000 L / 1 m3)
= 7.415 10⁻⁶ m³ (1000 L / 1 m3)
ΔΔ
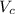 = 7.415 10⁻³ L
= 7.415 10⁻³ L