Answer: The concentration of A, B and C is 0.14 M, 0.24 M and 0.16 M respectively.
Step-by-step explanation:
Relation between standard Gibbs free energy and equilibrium constant follows:

where,
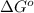 = standard Gibbs free energy = -3.87 kJ/mol = -3870 J/mol (Conversion factor: 1 kJ = 1000 J)
= standard Gibbs free energy = -3.87 kJ/mol = -3870 J/mol (Conversion factor: 1 kJ = 1000 J)
R = Gas constant =
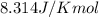
T = temperature =
![25^oC=[273+25]K=298K](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/6roip9my7lmduj9zgvg2iw8f5svzc0eagc.png)
 = equilibrium constant in terms of concentration
= equilibrium constant in terms of concentration
Putting values in above equation, we get:
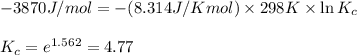
The given chemical reaction follows:
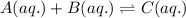
Initial: 0.30 0.40 0
At eqllm: 0.30-x 0.40-x x
The expression of
 for above equation follows:
for above equation follows:
![K_c=([C])/([A]* [B])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/7g0nqrh2vak2c3799y2cjknup22rdj4ixf.png)
We are given:

![[A]=0.30-x](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/wqngm9y9lepqrjo852ugx8fv2c36o4wymn.png)
![[B]=0.40-x](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/dbhlvbjofggrh6v12kfrs6xh7woic0admy.png)
![[C]=x](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/6znisasvebwiq1v6rrpru4miigtrtbjeaz.png)
Putting values in above expression, we get:
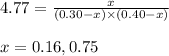
Neglecting the value of x = 0.75 because the equilibrium concentration cannot be greater than initial concentration.
So, concentration of A = (0.30 - x) = (0.30 - 0.16) = 0.14 M
Concentration of B = (0.40 - x) = (0.40 - 0.16) = 0.24 M
Concentration of C = x = 0.16 M
Hence, the concentration of A, B and C is 0.14 M, 0.24 M and 0.16 M respectively.