Step-by-step explanation:
(a). Let us assume that
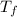 be the final temperature after mixing.
be the final temperature after mixing.
Hence,
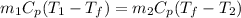
![T_(f) = ([T_(1) + (m_(2))/(m_(1)) * T_(2)])/(1 + (m_(2))/(m_(1)))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/yl1nuz3monn7j1zlvhosqpdzt0vukmoe4i.png)
The given data is as follows.
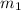 = 1 kg,
= 1 kg,
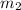 = 5 kg
= 5 kg
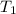 = 3100 K,
= 3100 K,
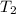 = 3600 K
= 3600 K
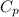 = 100 J/mol K
= 100 J/mol K
Hence, putting the given values into the above formula as follows.
![T_(f) = ([T_(1) + (m_(2))/(m_(1)) * T_(2)])/(1 + (m_(2))/(m_(1)))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/yl1nuz3monn7j1zlvhosqpdzt0vukmoe4i.png)
![T_(f) = ([3100 + ((5)/(1)) * 3600])/([1 + ((5)/(1)))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/hvkaswfxk6xaknr19lwebkrcmt55tqlv53.png)
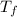 = 3516.7 K
= 3516.7 K
(b). As, entropy change of
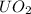 with
with
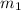 = 1 kg at 3100 K to attain 3516.7 K. Therefore, change in entropy will be calculated as follows.
= 1 kg at 3100 K to attain 3516.7 K. Therefore, change in entropy will be calculated as follows.
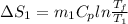
=
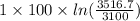
= 12.22 J/molK
Now, entropy change of
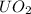 with
with
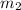 = 5kg at 3600 K to attain 3516.7 K. Hence,
= 5kg at 3600 K to attain 3516.7 K. Hence,
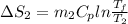
=
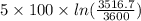
= -11.63 J/mol k
So, entropy of the total mass of
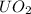 will be as follows.
will be as follows.
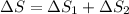
= 12.22 + (-11.63) J/mol K
= 0.59 J/mol K
(c). As, there is occurring an increase in the entropy. Therefore, the process is spontaneous.