Answer:
The net energy is 2.196 eV
Step-by-step explanation:
Basically, the energy of an atom increases when it absorbs a photon. In addition, the wavelength of the emitted photon is longer such that the atom absorbed a net energy in the process.
Using:
ΔE = h*c*(1/λ
 - 1/λ
- 1/λ
 )
)
where:
ΔE is the net energy in eV (electron-volt). 1 eV is equivalent to 1.602*
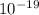 J.
J.
h = 4.135*
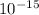 eVs
eVs
c = 3*
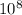 m/s
m/s
λ
 = 300 nm = 300*
= 300 nm = 300*
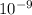 m
m
λ
 = 640 nm = 640*
= 640 nm = 640*
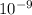 m
m
Thus:
ΔE = 4.135*
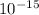 eVs*3*
eVs*3*
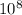 m/s*(
m/s*(
 )
)
ΔE = 4.135*
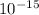 *3*
*3*
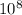 *1.77*
*1.77*
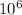 eV = 2.196 eV
eV = 2.196 eV