To solve this exercise, it is necessary to apply the concepts related to energy conservation of both incidence and kinetic.
Let's define
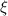 as the energy needed to remove the electron (Work function previously given)
as the energy needed to remove the electron (Work function previously given)
And the Kinetic energy of the Photon the energy needed to add it to the total incidence energy. So, we have,
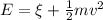
Where,
m= mass
v= velocity
E = Energy of an incident photon
Then we have that

Equation both equations we have that
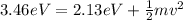
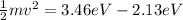
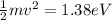
Therefore the maximum kinetic energy will be 1.38eV