Answer : The cell potential for this reaction is 0.50 V
Explanation :
The given cell reactions is:

The half-cell reactions are:
Oxidation half reaction (anode):
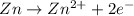
Reduction half reaction (cathode):
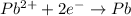
First we have to calculate the cell potential for this reaction.
Using Nernest equation :
![E_(cell)=E^o_(cell)-(2.303RT)/(nF)\log ([Zn^(2+)])/([Pb^(2+)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ey524n45if5gq1vbque83wtwqwevjo1g54.png)
where,
F = Faraday constant = 96500 C
R = gas constant = 8.314 J/mol.K
T = room temperature =
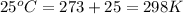
n = number of electrons in oxidation-reduction reaction = 2
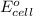 = standard electrode potential of the cell = +0.63 V
= standard electrode potential of the cell = +0.63 V
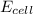 = cell potential for the reaction = ?
= cell potential for the reaction = ?
![[Zn^(2+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/r2c6mtit38a2tcs4gpb6emu5lf5fgq74tw.png) = 3.5 M
= 3.5 M
![[Pb^(2+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/b4acgmyvdeowtue90jvnyrf5e2r0w481qd.png) =
=
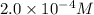
Now put all the given values in the above equation, we get:
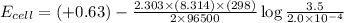
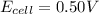
Therefore, the cell potential for this reaction is 0.50 V