Answer:
b. 0.75 mm
Step-by-step explanation:
The distance between antinodes d is half the wavelength
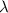 . We can obtain the wavelength with the formula
. We can obtain the wavelength with the formula
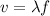 , where f is the frequency given (
, where f is the frequency given (
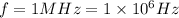 ) and v is the speed of sound in body tissues (v=1540m/s), so putting all together we have:
) and v is the speed of sound in body tissues (v=1540m/s), so putting all together we have:
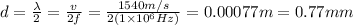
which is very close to the 0.75mm option.