Answer:
For a: The balanced chemical equation is written below.
For b: The corrosion of iron pipe will take place in the presence of zinc.
For c: Zinc will not protect iron pipe from corrosion.
Step-by-step explanation:
The given half reaction follows:
The substance having highest positive
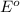 potential will always get reduced and will undergo reduction reaction. Here, zinc will undergo reduction reaction will get reduced.
potential will always get reduced and will undergo reduction reaction. Here, zinc will undergo reduction reaction will get reduced.
Oxidation half reaction:
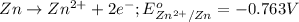
Reduction half reaction:
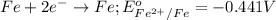
The balanced chemical equation follows:
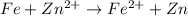
For a reaction to be spontaneous (thermodynamically feasible) , the standard electrode potential must be positive.
To calculate the
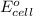 of the reaction, we use the equation:
of the reaction, we use the equation:
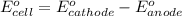
Substance getting oxidized always act as anode and the one getting reduced always act as cathode.
Calculating the
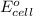 using above equation, we get:
using above equation, we get:
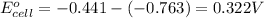
As, the EMF is coming out to be positive, the reaction will be thermodynamically feasible and corrosion of iron pipe will take place in the presence of zinc.
As, the EMF of the cell is positive, the zinc will not protect the iron pipe from corrosion and the reaction will take place.