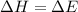Answer : Only option A shows
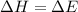
Explanation :
Formula used :
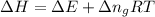
 = change in enthalpy
= change in enthalpy
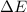 = change in internal energy
= change in internal energy
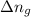 = change in moles
= change in moles
R = gas constant = 8.314 J/mol.K
T = temperature
According to the question,
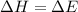 when the value of
when the value of
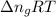 will be zero.
will be zero.
Now we have to determine the value of
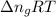 for the following cases.
for the following cases.
(A)
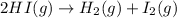 at atmospheric pressure.
at atmospheric pressure.
In this case:
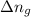 = change in moles
= change in moles
Change in moles = Number of moles of product side - Number of moles of reactant side
According to the reaction:
Change in moles = (1+1) - 2 = 2 - 2 = 0 mole
That means, value of
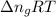 = 0
= 0
So, in this process
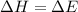
(B) Two moles of ammonia gas are cooled from 325 °C to 300 °C at 1.2 atm.
In this case:
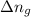 = change in moles = 2
= change in moles = 2
That means, value of
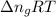 ≠ 0
≠ 0
So, in this process
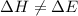
(C)
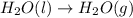 at 100 °C at atmospheric pressure.
at 100 °C at atmospheric pressure.
In this case:
Change in moles = Number of moles of product side - Number of moles of reactant side
According to the reaction:
Change in moles = 1 - 0 = 1 mole
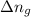 = change in moles = 1
= change in moles = 1
That means, value of
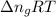 ≠ 0
≠ 0
So, in this process
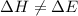
(D)
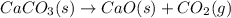 at 800 °C at atmospheric pressure.
at 800 °C at atmospheric pressure.
In this case:
Change in moles = Number of moles of product side - Number of moles of reactant side
According to the reaction:
Change in moles = 1 - 0 = 1 mole
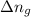 = change in moles = 1
= change in moles = 1
That means, value of
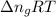 ≠ 0
≠ 0
So, in this process
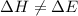
(E)
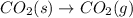 at atmospheric pressure.
at atmospheric pressure.
In this case:
Change in moles = Number of moles of product side - Number of moles of reactant side
According to the reaction:
Change in moles = 1 - 0 = 1 mole
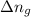 = change in moles = 1
= change in moles = 1
That means, value of
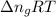 ≠ 0
≠ 0
So, in this process
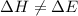
Hence, from this we conclude that, only option A shows