Answer: The number of valence electrons that M must have is 1.
Step-by-step explanation:
The chemical equation for the reaction of metal oxide with water follows:

The reaction of metal hydroxide with hydrochloric acid follows:
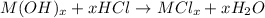
To calculate the number of moles for given molarity, we use the equation:
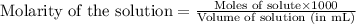 .....(1)
.....(1)
Molarity of metal hydroxide solution = 0.40 M
Volume of solution = 75 mL
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
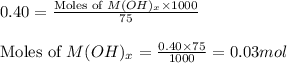
Molarity of HCl = 1.1 M
Volume of solution = 27 mL
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
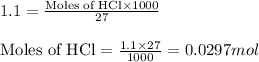
To calculate the value of 'x', we divide the number of moles of HCl by number of moles of metal hydroxide, we get:

Hence, the number of valence electrons that M must have is 1.