Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that,
Average power per unit mass generated by Lance,
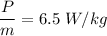
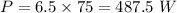
(a) Distance to cover race,
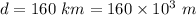
Average speed of the person, v = 11 m/s
If t is the time taken to cover the race.
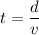
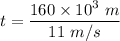
t = 14545.46 s
Let W is the work done. The relation between the work done and the power is given by :
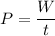
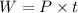
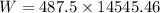
W = 7090911.75 J
(b) Since,
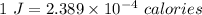
So, in 7090911.75 J,
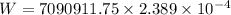
W = 1694.01 J
Hence, this is the required solution.