Answer:
Zero
Step-by-step explanation:
To solve the problem, we just need to analyze the forces acting on the top cube.
There are two forces acting on it:
- The force of gravity (the weight of the cube), downward, which is
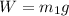
where
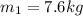 is the mass of the cube
is the mass of the cube
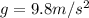 is the acceleration of gravity
is the acceleration of gravity
- The normal reaction exerted by the bottom cube on the top cube, upward, which we indicate with R
So, the equation of the forces for the top cube is
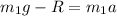
where
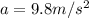 is the acceleration of the cube, since it is in free fall
is the acceleration of the cube, since it is in free fall
Solving for R, we find:
