Answer:
2065.005 m/s²
Step-by-step explanation:
t = Time taken
u = Initial velocity
v = Final velocity
s = Displacement
a = Acceleration
g = Acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s²
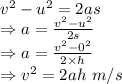
Now H-h = 42.3 - 0.2 = 42.1 cm = 0.421 m
The final velocity will be the initial velocity
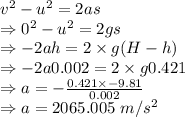
Acceleration of the frog is 2065.005 m/s²