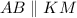Answer:
See explanation
Explanation:
1. BK is an angle B bisector, then
 (definition of angle bisector)
(definition of angle bisector)
2. BM = MK, then
triangle BMK is isosceles triangle with base BK.
3. Angles adjacent to the base of isosceles triangle are congruent, then

Note that angle MBK is the same as angle CBK.
4. By substitution property,
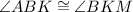
5. By alternate interior angles theorem,
if
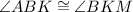 , then
, then