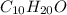Answer:
The empirical formula is =
Step-by-step explanation:
Mass of water obtained =
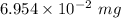
Also, 1 mg =
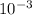 g
g
So, mass of water =
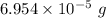
Molar mass of water = 18 g/mol
Moles of
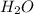 =
=
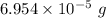 /18 g/mol = 3.8634×10⁻⁶ moles
/18 g/mol = 3.8634×10⁻⁶ moles
2 moles of hydrogen atoms are present in 1 mole of water. So,
Moles of H = 2 x 3.8634×10⁻⁶ = 7.7267×10⁻⁶ moles
Molar mass of H atom = 1.008 g/mol
Mass of H in molecule = 7.7267×10⁻⁶ x 1.008 = 7.6653×10⁻⁶ g
Mass of carbon dioxide obtained = 0.1697 mg
Also, 1 mg =
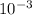 g
g
So, mass of carbon dioxide =
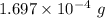
Molar mass of carbon dioxide = 44.01 g/mol
Moles of
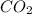 =
=
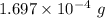 /44.01 g/mol = 3.856×10⁻⁶ moles
/44.01 g/mol = 3.856×10⁻⁶ moles
1 mole of carbon atoms are present in 1 mole of carbon dioxide. So,
Moles of C = 3.856×10⁻⁶ moles
Molar mass of C atom = 12.0107 g/mol
Mass of C in molecule = 3.856×10⁻⁶ x 12.0107 = 46.3132 ×10⁻⁶ g
Given that the Menthol only contains hydrogen, oxygen and carbon. So,
Mass of O in the sample = Total mass - Mass of C - Mass of H
Mass of the sample =
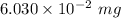
Also, 1 mg =
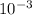 g
g
So, mass of sample =
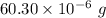
Mass of O in sample = ( 60.30 - 7.6653 - 46.3132 ) ×10⁻⁶ g= 6.3215×10⁻⁶ g
Molar mass of O = 15.999 g/mol
Moles of O = 6.3215×10⁻⁶ / 15.999 = 0.3951×10⁻⁶ moles
Taking the simplest ratio for H, O and C as:
7.7267×10⁻⁶ : 0.3951×10⁻⁶ : 3.856×10⁻⁶
= 20 : 1 : 10
The empirical formula is =