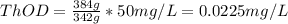Answer:
a) 213.3 mg/L
b) 62.61 mg/L
c) 0.0225 mg/L
Step-by-step explanation:
Theoretical oxygen demand (ThOD)is essentially the amount of oxygen required for the complete degradation of a given compound into the final oxidized products
a) Given:
Concentration of acetic acid,
![[CH3COOH]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/3e8bpuyss8kgkspaqd7akwlsbg4h3n8f8i.png) = 200 mg/L
= 200 mg/L
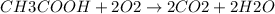
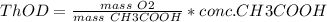
Based on the reaction stoichiometry:
mass of
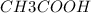 = 60 g
= 60 g
mass of
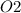 = 2(32) = 64 g
= 2(32) = 64 g
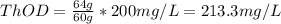
b) Given:
Concentration of ethanol,
![[C2H5OH]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/7kyetxh74wi913fe1wjnyi4mfxkbpapdm9.png) = 30 mg/L
= 30 mg/L
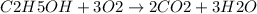
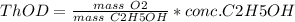
Based on the reaction stoichiometry:
mass of
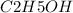 = 46 g
= 46 g
mass of
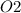 = 3(32) = 96 g
= 3(32) = 96 g
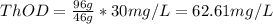
c) Given:
Concentration of sucrose,
![[C12H22O11]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/6jypp584aay0vcv85jynst37sb35ttpv7z.png) = 50 mg/L
= 50 mg/L
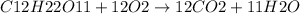
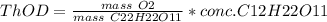
Based on the reaction stoichiometry:
mass of
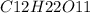 = 342 g
= 342 g
mass of
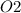 = 12(32) = 384 g
= 12(32) = 384 g