Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that the initial mass of benznene is 7.9286 g
Mass of benzene left = 5.9987 g
So, mass of benzene with which gas get saturated will be calculated as follows.
= 7.9286 g - 5.9987 g = 1.9299 g
Therefore, moles of benzene with which gas get saturated =
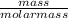
=
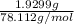
= 0.0247 moles
Temperature =
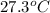 = 27.3 + 273.15 = 300.45 K
= 27.3 + 273.15 = 300.45 K
Volume = 5.01 L
So, according to ideal gas equation PV = nRT
Putting the given values into the ideal gas equation as follows.
PV = nRT
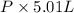 =
=
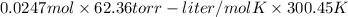
P =
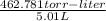
= 92.371 torr
Hence, we can conclude that vapor pressure of benzene is 92.371 torr.