Answer:
6.57 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
From work energy theorem, work done = W = Change in Kinetic energy
W =
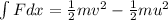
here v is the final velocity and u is the initial velocity and F is the force.
Horizontal component of the force is considered here since motion is along the horizontal (X) direction. So cos 31
Work done =
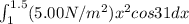
⇒
![(5)(0.866)[(1.5^(3))/(3)-(1^(3))/(3)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/1ui8phgxk5x0xyvyu6h3q53c1hrzdm3rp4.png) =3.39 J
=3.39 J
 = 3.39
= 3.39
⇒
 = 3.30
= 3.30
⇒ Speed at x = 1.50 m = v = 6.57 m/s