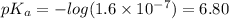Answer:
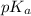 of HA is 6.80
of HA is 6.80
Step-by-step explanation:
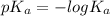
Acid dissociation constant (
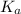 ) of HA is represented as-
) of HA is represented as-
![K_(a)=([H^(+)][A^(-)])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/zagzd1d9lkebolm87rlz12gkd8fco4umqf.png)
Where species inside third bracket represents equilibrium concentrations
Now, plug in all the given equilibrium concentration into above equation-
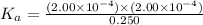
So,
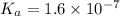
Hence