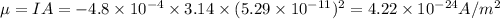Answer:
(a)
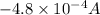 (B)
(B)
Step-by-step explanation:
We have given the the speed of the electron =10^6 m/sec
The time period of the electron is given by
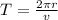 where r is the Bohr radius, which is equal to
where r is the Bohr radius, which is equal to
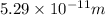
So time period
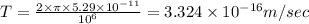
(A) We know that current
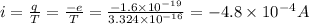
(B) Magnetic moment is given by
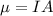 , where I is current and A is area
, where I is current and A is area
So