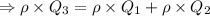Answer:
The statement regarding the mass rate of flow is mathematically represented as follows
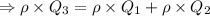
Explanation:
A junction of 3 pipes with indicated mass rates of flow is indicated in the attached figure
As a basic sense of intuition we know that the mass of the water that is in the pipe junction at any instant of time is conserved as the junction does not accumulate any mass.
The above statement can be mathematically written as
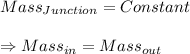
this is known as equation of conservation of mass / Equation of continuity.
Now we know that in a time 't' the volume that enter's the Junction 'O' is
1) From pipe 1 =
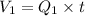
1) From pipe 2 =
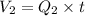
Mass leaving the junction 'O' in the same time equals
From pipe 3 =
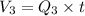
From the basic relation of density, volume and mass we have
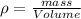
Using the above relations in our basic equation of continuity we obtain
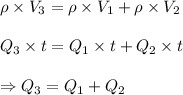
Thus the mass flow rate equation becomes