Answer : The mass of
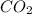 produced will be, 5.3 grams.
produced will be, 5.3 grams.
Explanation : Given,
Mass of
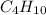 = 1.74 g
= 1.74 g
Mass of
 = 11 g
= 11 g
Molar mass of
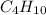 = 58 g/mole
= 58 g/mole
Molar mass of
 = 32 g/mole
= 32 g/mole
Molar mass of
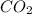 = 44 g/mole
= 44 g/mole
First we have to calculate the moles of
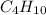 and
and
 .
.
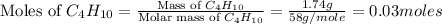
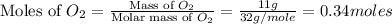
Now we have to calculate the limiting and excess reagent.
The balanced chemical reaction is,
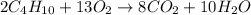
From the balanced reaction we conclude that
As, 2 moles of
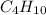 react with 13 mole of
react with 13 mole of

So, 0.03 moles of
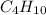 react with
react with
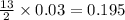 moles of
moles of

From this we conclude that,
 is an excess reagent because the given moles are greater than the required moles and
is an excess reagent because the given moles are greater than the required moles and
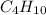 is a limiting reagent and it limits the formation of product.
is a limiting reagent and it limits the formation of product.
Now we have to calculate the moles of
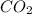 .
.
As, 2 moles of
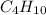 react to give 8 moles of
react to give 8 moles of
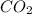
So, 0.03 moles of
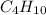 react to give
react to give
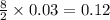 moles of
moles of
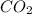
Now we have to calculate the mass of
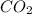 .
.
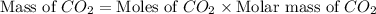
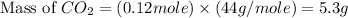
Therefore, the mass of
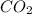 produced will be, 5.3 grams.
produced will be, 5.3 grams.