Answer:
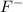
Step-by-step explanation:
The weak acid HF is in solution with dissolved NaF; NaF is an ionic compound, so it will dissolve by dissociating its ions; this solution reaction is:
NaF⇒
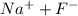
So, initially there will be these species in solution:
-NaF
-
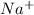
-
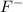
If we add HCl, which is a strong acid, it will dissociate completely (that is the characteristic of a strong acid) in ions H+ and Cl-:
HCl⇒
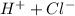
So, we are finally adding ions
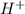 and
and
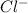 .
.
We are asked which ion will react with the
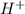 released by HCl acid. We should think just about the anions (negative ions) because we require an electron donor to create a bond with H+, so it won't be on solution as H+. We just have two anions in solution:
released by HCl acid. We should think just about the anions (negative ions) because we require an electron donor to create a bond with H+, so it won't be on solution as H+. We just have two anions in solution:
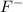 and
and
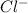 .
.
If
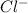 bonded to
bonded to
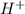 it would form HCl, but we saw that HCl is a strong acid which always dissociate completely in aqueous solution; so
it would form HCl, but we saw that HCl is a strong acid which always dissociate completely in aqueous solution; so
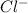 will never bond to
will never bond to
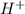 . Finally,
. Finally,
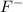 can bond
can bond
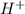 giving HF as a result; it is possible because HF is a weak acid, and HF can be, in fact, present in an aqueous solution; the
giving HF as a result; it is possible because HF is a weak acid, and HF can be, in fact, present in an aqueous solution; the
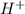 ions will be changed to HF and the pH (which depends only on
ions will be changed to HF and the pH (which depends only on
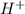 concentration) will not change.
concentration) will not change.