Answer:
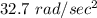
Step-by-step explanation:
We have given the acceleration of the cord is
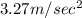 and acceleration due to gravity is
and acceleration due to gravity is
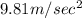 there is a relation between the angular acceleration and the linear acceleration that is
there is a relation between the angular acceleration and the linear acceleration that is
Linear acceleration = angular acceleration × radius
We have given radius R = 10 cm =0.1 m
So
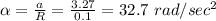 here α is angular acceleration a is linear acceleration and R is radius
here α is angular acceleration a is linear acceleration and R is radius