Answer: The chemical equations are given below.
Step-by-step explanation:
- For a: Fe is heated in an atmosphere of steam.
The chemical equation follows:
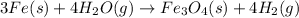
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
3 moles of iron reacts with 4 moles of steam to produce 1 mole of iron (II,III) oxide and 4 moles of hydrogen.
- For b: NaOH is added to a solution of
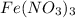
The chemical equation follows:
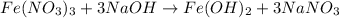
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of iron nitrate reacts with 3 moles of sodium hydroxide to produce 1 mole of iron hydroxide and 3 moles of sodium nitrate.
- For c:
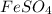 is added to an acidic solution of
is added to an acidic solution of
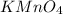
The chemical equation follows:
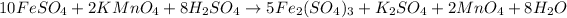
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
10 moles of iron(II) sulfate reacts with 2 moles of potassium permangante and 8 moles of sulfuric acid to produce 5 moles of iron(III) sulfate, 1 mole of potassium sulfate, 2 moles of manganese oxide and 8 moles of water.
- For d: Fe is added to a dilute solution of
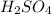
The chemical equation follows:
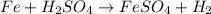
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of iron reacts with 1 mole of sulfuric acid to produce 1 mole of iron sulfate and 1 mole of hydrogen gas.
- For e: A solution of
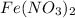 and
and
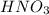 is allowed to stand in air.
is allowed to stand in air.
The chemical equation follows:
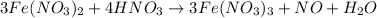
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
3 moles of iron(II) nitrate reacts with 4 moles of nitric acid to produce 3 moles of iron(III) nitrate, 1 mole of nitric oxide and 1 mole of water.
- For f:
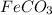 is added to a solution of
is added to a solution of
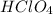
The chemical equation follows:
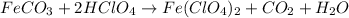
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of iron(II) carbonate reacts with 2 moles of perchloric acid to produce 1 moles of iron(II) perchlorate, 1 mole of carbon dioxide and 1 mole of water.
- For g: Fe is heated in air
The chemical equation follows:
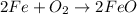
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
2 moles of iron reacts with 1 mole of oxygen gas to produce 2 moles of iron(II) oxide.
Hence, the chemical equations are given above.