Answer:
Part a)
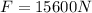
Part b)
force is 21.2 times more than the weight of the person
Step-by-step explanation:
Part a)
As it is given that the distance after which he stopped is given as
d = 1.50 cm
here finally it stops so final speed is given as
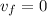
initial speed is given as
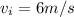
now by the equation of kinematics we know that
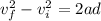
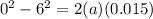
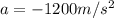
Now the force on the leg is given as
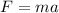
m = mass of leg = 13 kg
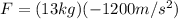
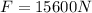
Part b)
Force due to weight of the object
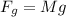
here we know
M = 75.0 kg
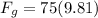
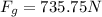
Now we know that the ratio of the weight with the force on leg is given as
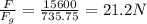
so force is 21.2 times more than the weight of the person