Answer: A) 0.10 mol
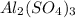
Step-by-step explanation:
As the relative lowering of vapor pressure is directly proportional to the amount of dissolved solute.
The formula for relative lowering of vapor pressure will be,
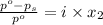
where,
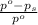 = relative lowering in vapor pressure
= relative lowering in vapor pressure
i = Van'T Hoff factor
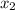 = mole fraction of solute
= mole fraction of solute
1. For 0.10 mol
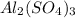
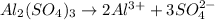
, i= 5 as it is a electrolyte and dissociate to give 5 ions. and concentration of ions will be
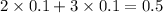
2. For 0.10 mol sucrose
, i= 1 as it is a non electrolyte and does not dissociate, concentration of ions will be
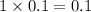
3. For 0.40 mol glucose
, i= 1 as it is a non electrolyte and does not dissociate, concentration of ions will be
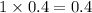
4. For 0.2
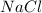
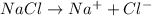
, i= 2 as it is a electrolyte and dissociate to give 2 ions, concentration of ions will be
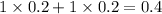
Thus as concentration of solute is highest for
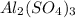 , the vapor pressure will be lowest.
, the vapor pressure will be lowest.