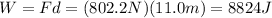(a) 9305 J
Let's start by finding the acceleration of the spelunker, through the following equation:
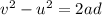
where
v = 2.40 m/s is the final velocity
u = 0 is the initial velocity
a is the acceleration
d = 11.0 m is the distance covered
Solving for a,
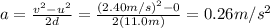
Now we can find the force lifting the spelunker. The equation for Newton's second law applied to the spelunker is:
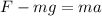
where
F is the lifting force
m = 84.0 kg is the mass of the spelunker
g = 9.81 m/s^2 is the acceleration due to gravity
a = 0.26 m/s^2 is the acceleration
Solving for F,
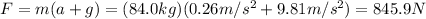
And now we can finally find the work done on the spelunker by the lifting force F:
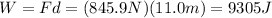
(b) 9064 J
In this case, the speed is constant, so the acceleration is zero. So Newton's second Law becomes
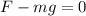
From which we find
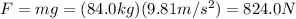
And so the work done is
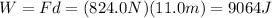
(c) 8824 J
The acceleration of the spelunker here is given by
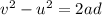
where
v = 0 is the final velocity
u = 2.40 m/s is the initial velocity
a is the acceleration
d = 11.0 m is the distance covered
Solving for a,
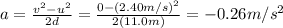
Newton's second law applied to the spelunker is:
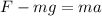
where
F is the lifting force
m = 84.0 kg is the mass of the spelunker
g = 9.81 m/s^2 is the acceleration due to gravity
a = -0.26 m/s^2 is the acceleration
Solving for F,
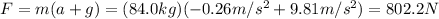
And now we can finally find the work done on the spelunker by the lifting force F: