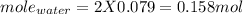The reaction is
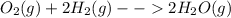
Thus from each mole of oxygen we will get two moles of water, if we are taking excess of hydrogen. As we are taking hydrogen in excess the oxygen is the limiting reagent
Let us calculate the moles of oxygen used from ideal gas equation
PV=nRT
where
P = pressure = 122.3 kPascals = 1.21 atm
V = volume = 5.4 L
T = temperature =
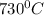 =1003K
=1003K
n=moles=?
R=gas constant = 0.0821 Latm / mol K
putting values
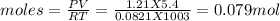
therefore moles of water formed will be twice of moles of oxygen taken