Answer:
The speed of the ball B is 6.4 m/s. The direction is 50 degrees counterclockwise.
Step-by-step explanation:
Assuming the collision is elastic, use the conservation of momentum to solve this problem. The conservation law implies that:
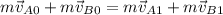
(the total momentum of the two balls is the same before (index 0) and after (index 1) the collision). Since B is stationary and A and B have the same mass, this simplifies to:
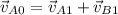
and allows us to determine the velocity of ball B after the collision:
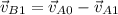
The above involves vectors. Your problem suggests to use the component method, which I am assuming means solving the above equation separately along the x and y axes. Define x to align with the original line of motion of the ball A before the collision, and y to be perpendicular to x, pointing up:
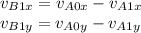
We just need to compute the x- and y-components of the known velocity of the ball A. Drs. Sine and Cosine come to help here.
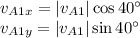
so
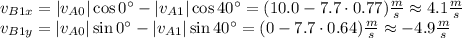
The speed of the ball B is
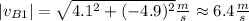 . The direction (angle from horizontal) is
. The direction (angle from horizontal) is
 , i.e., 50 degrees counterclockwise.
, i.e., 50 degrees counterclockwise.