The rate of a reaction would be one-fourth.
Further explanation
Given
Rate law-r₁ = k [NO]²[H2]
Required
The rate of a reaction
Solution
The reaction rate (v) shows the change in the concentration of the substance (changes in addition to concentrations for reaction products or changes in concentration reduction for reactants) per unit time.
Can be formulated:
Reaction: aA ---> bB
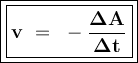
or
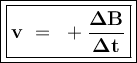
The concentration of NO were halved, so the rate :
![\tt r_2=k[(1)/(2)No]^2[H_2]\\\\r_2=(1)/(4)k.[No]^2[H_2]\\\\r_2=(1)/(4)r_1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ez889c99i94uqgmf52nepu0udxd1im2a0w.png)